Until the lan hellos are received from the neighbor the adjacency remains in the down state.
When the hellos are received from the neighbor the local router takes a note of the system address of the neighbor
This does not ensure bidirectional communication, then the local router includes the system mac address of the neighbor in the IS neighbor TLV. When the remote router views its own
mac address in the hello message received from the remote end the adjacency is changed to full.
Different types of adjacency are given above.
In the case of P2P adjacency the router notes the system id from the source id field from the hello it received from the neighbor and populates this with the neighbor system id field and local circuit id in the extended local circuit id field it changes the neighborship to up.
Neighbor system id and the neighbor extended local circuit id field is important for creating adjacency with the neighbor first the heelo packets are sent
In the above figure router R2 receives the hello but it has not seen its own circuit id in the neighbor ext circuit id field and its own system address in the neighbor system id field since it receives the hello it changes to init state. It notes the neighbor system address from the source id field.
In the above figure the router sees it own system id in the neighbor system id field and its own circuit id in the neighbor system id field and changes the state to up.
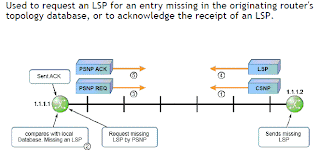
CSNP are then sent as seen in the below figure, two CSNP will be sent if the link is L1/L2