Classification direct the traffic to different Forwarding Classes.
Classification can be done in 2 ways
1> Multifield:- Information on the frame header like Ether type, mac address L3 fields like ip address, prefix and the protocol number , TCP/UDP port number it can also be done on the basis of port numbers and control fields.
The second option it is done on the basis of Behavariol Aggregate
Behavariol Aggregate includes the following:-
Classification can be done on L2, ie traffic which are tagged. In this case the classification is based on dot1p bits. There are 3 bits in user priority which are used for classification, these 2 bits probides 8 different classification levels.
Layer 3 Classification :-
This is done on the basis of Tos bits.
There are two ways to implement this
1> IP precedence which uses the first 3 bits of the Tos field leading to 8 different classes. The next 3 bits can also be used however it increases the sensitivity of the traffic and is not widely used.
2> DSCP:- 6 bits of the Tos field are used. The first 3 bits are used for precedence and the next 3 bits are used for the drop probability.
The two most important DSCP PHB are
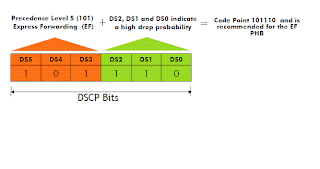
1> Expedited forwarding:- This has a very high precedence level 5 with a very high drop probability. This can be used in the case for very sensitive traffic like voice. This creates kind of virtual connection between two endpoints.
2> Assured forwarding:- It has different classes as given below:-
In the case of a congested network, the node tries to protect packets with lower drop precedence values, by dropping packets which have a higher drop precedence value.
MPLS traffic:-
For MPLS traffic exp bits are used to classify the traffic.
Routers can use pipe mode in this case the first 3 DSCP bits are copied to the EXP bits, when the packet enters the MPLS domain, after the exp values are modified inside the mpls domain when the packet egressses the network the exp values are copied back to the exp bits.
In the case of uniform mode the first 3 dscp bits are copied to the exp bits however when the packet egresses out of the network the modified exp bits are stripped off, and the original dscp values are retained.
Classification used in Alcatel routers this is done in the sap ingress policy by default sap ingress policy already exists which is called as 1
The below example gives a snapshot of how the sap ingress policy is applied, as we can notice match dot1p top refers to matching the priority bits with the top tag and bottom refers to matching it with the bottom tag.
After classification traffic is mapped to different forwarding classes.
As discussed before traffic are classified to 8 different forwarding classes the different FC are given below:-
Mapping of forwarding classes to SAP ingress is shown below:-










No comments:
Post a Comment